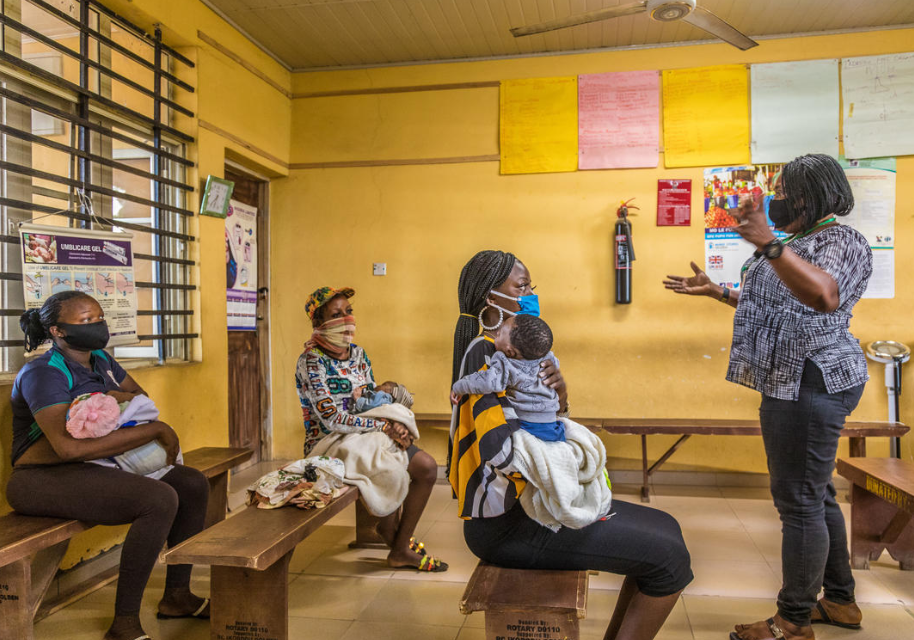
This research project aims to identify the best screening strategies for precancerous lesions of cervical cancer among women living with HIV in Cameroon. It will evaluate several possible adaptations of strategies to the context and the performance of different tests to complement the initial HPV test.
Context
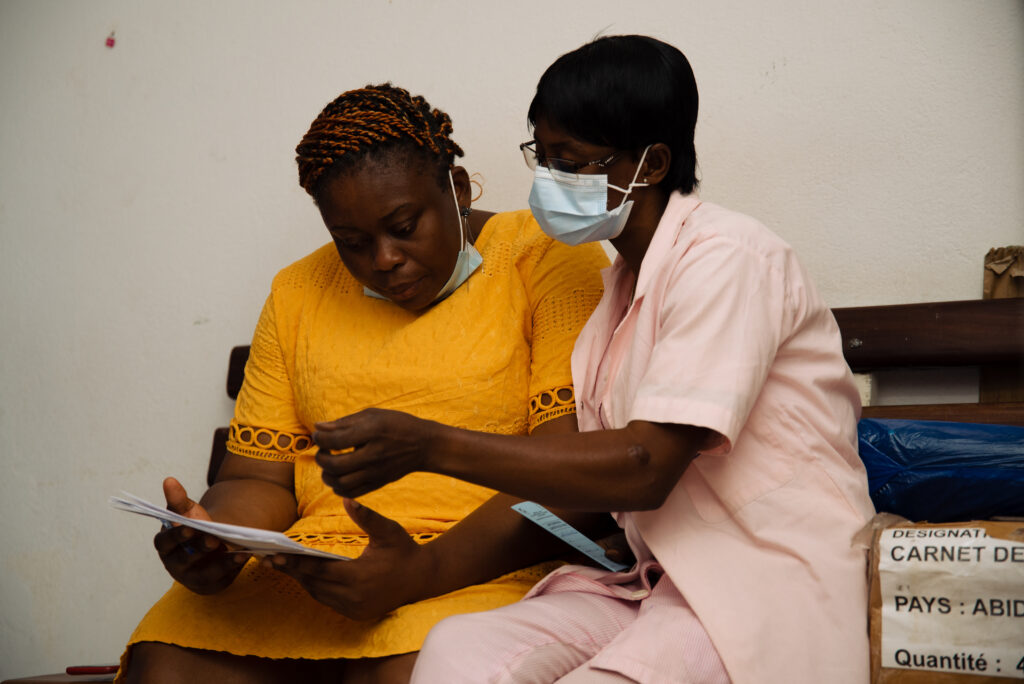
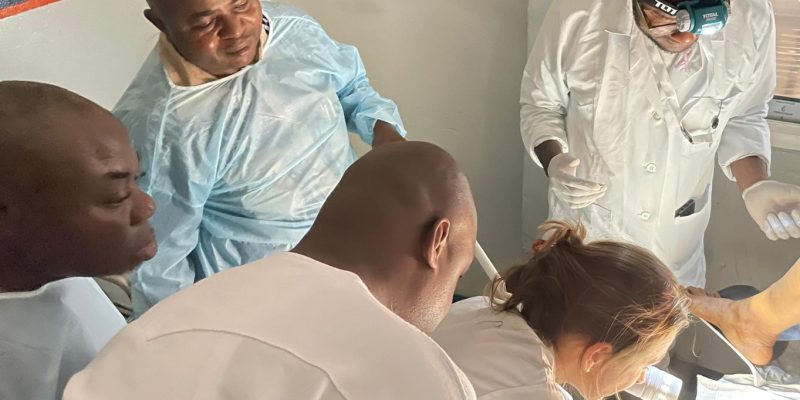
Cervical cancer is a major cause of mortality among women living with HIV in developing countries. It is possible to screen for human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, which are the cause of this disease. Since these infections are common among women living with HIV, the WHO recommends conducting a second test, as not all HPV infections lead to precancerous lesions. Therefore, secondary triage is desirable to avoid unnecessary treatment for some women carrying HPV. As part of the WHO’s global initiative for the elimination of cervical cancer, this research project aims to determine the best screening strategies to ensure maximum coverage at each stage of the screening cascade, particularly in the context of decentralized care.
Description
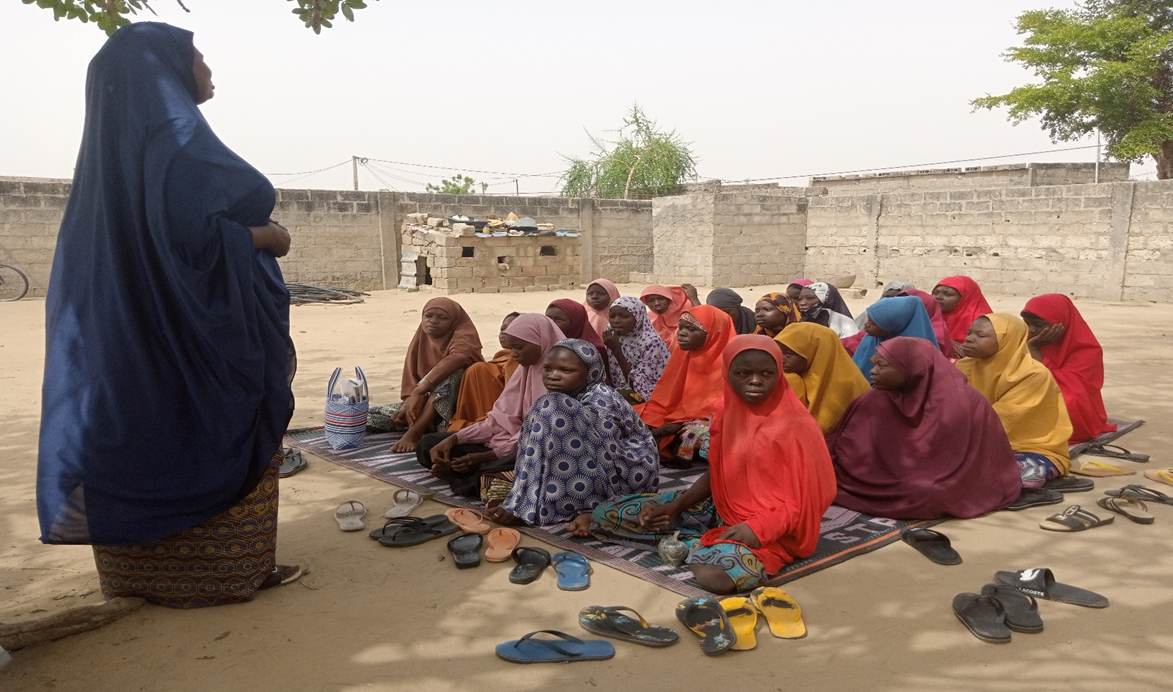
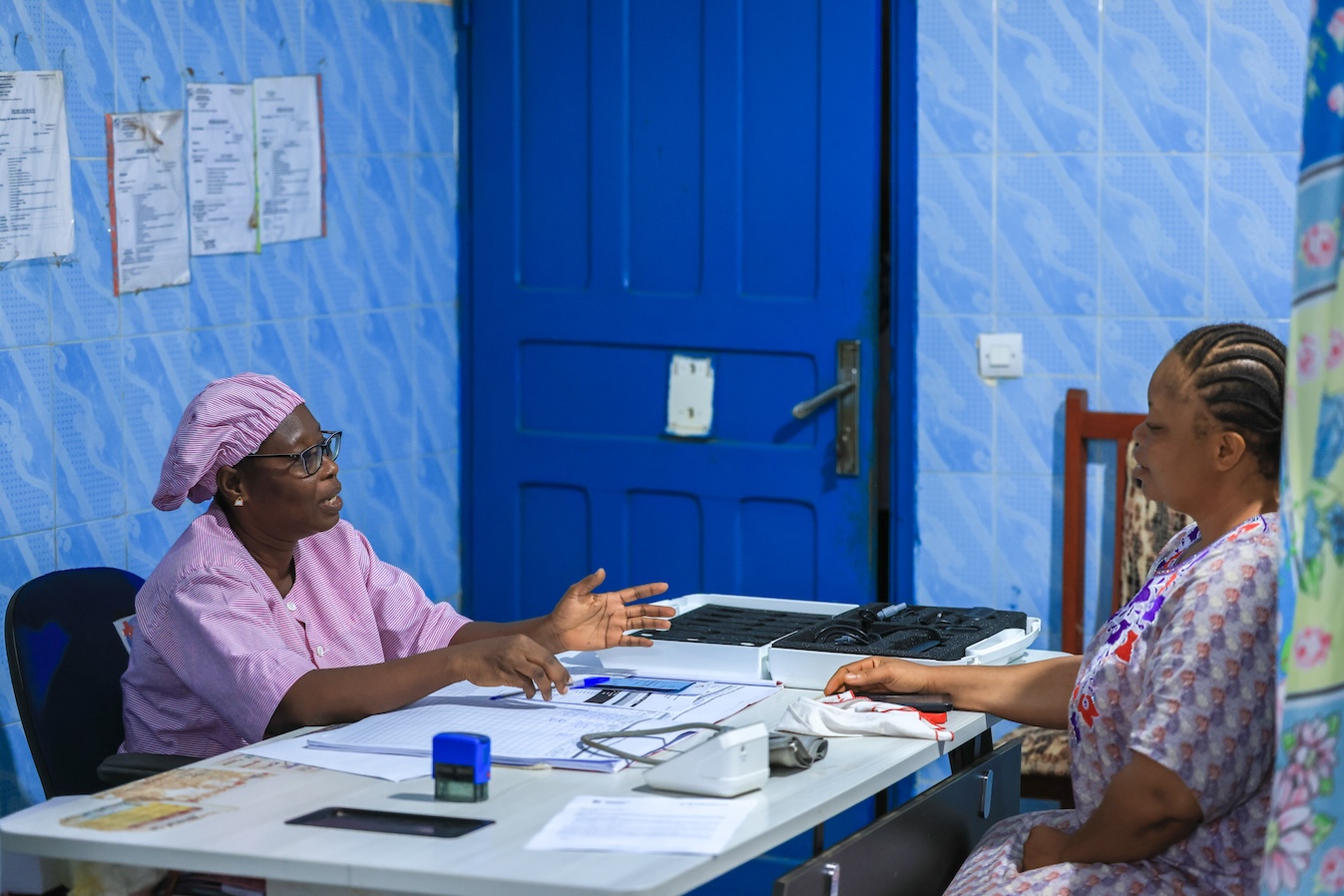
The overall objective of this operational research project is to develop, implement, and evaluate different methods for cervical cancer screening among women living with HIV. It compares centralized and decentralized screening approaches, as well as standard triage test techniques, simplified methods, and those relying on artificial intelligence. The aim is to develop a more effective and acceptable cervical cancer screening method for patients, using simple and standardized interpretation criteria, and to identify suitable implementation strategies. A participatory approach, combining quantitative and qualitative methods, will be adopted to conduct the research.
Impact
This research provides policymakers and key stakeholders with evidence and data regarding the most effective cervical cancer screening strategy to implement.